- Linux
- Dataflex
- Networking
- Postgresql
- Proxmox
- Windows
- Wordpress
Understanding and Fixing MTU, Path MTU Discovery, and MSS Clamping Issues
Understanding and Fixing MTU, Path MTU Discovery, and MSS Clamping Issues
In modern networks, performance and reliability depend on more than just link speed. One of the most common — yet often overlooked — causes of slow or broken connections is an MTU mismatch.
This guide walks through how MTU, Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD), and MSS Clamping work, the symptoms of MTU-related issues, and how to find and fix the correct MTU on your network.
What Is MTU?
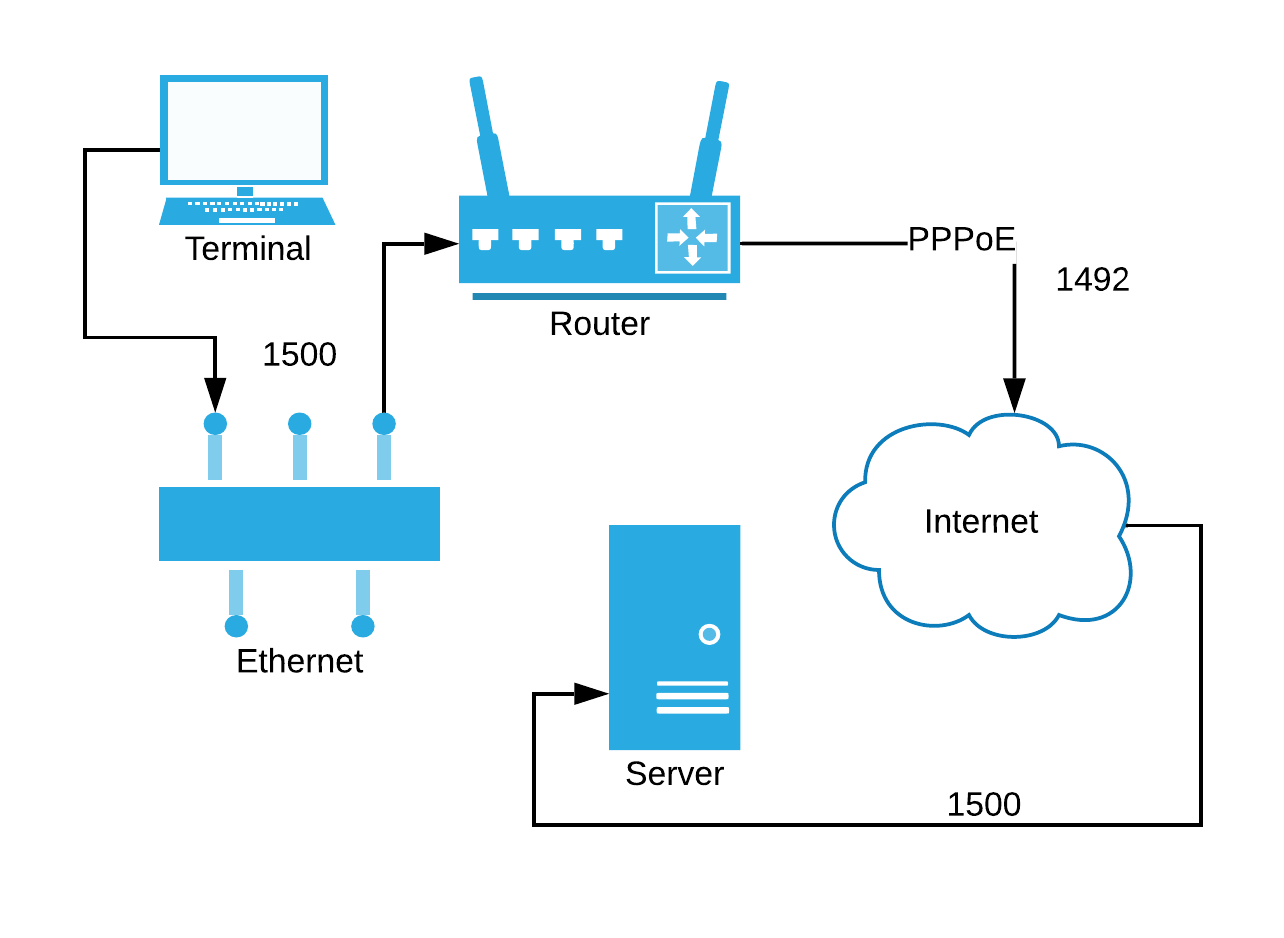
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) defines the largest packet size a network interface can send in a single frame.
Different network technologies use different MTUs:
| Technology | Typical MTU |
|---|---|
| Ethernet | 1500 bytes |
| Ethernet (Jumbo Frames) | 9000–9202 bytes |
| PPPoE | 1492 bytes |
| WLAN | 2304 bytes |
When a packet exceeds the MTU, it must be fragmented — split into smaller chunks — before it can be transmitted. While fragmentation allows data to move across diverse links, it adds CPU overhead, increases latency, and can lead to dropped packets or timeouts.
Why MTU Matters
A mismatch in MTU sizes along a route can lead to partial connections or intermittent failures.
Common symptoms include:
- SSH or SCP sessions timing out
- Websites that partially load or hang
- Chat applications unable to send messages
- SSL/TLS negotiation failures (e.g., connecting to
packages.gitlab.com) - Random client disconnections
If these issues seem familiar, MTU could be the culprit.
How Path MTU Discovery Works
Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD) determines the smallest MTU across all hops between source and destination. It works like this:
- The sender transmits packets with the "Don’t Fragment (DF)" bit set.
- If a router along the path cannot forward the packet due to size, it replies with an ICMP "Fragmentation needed" message.
- The sender lowers its packet size and retries until it reaches the destination successfully.
This automatic negotiation keeps communication efficient — as long as ICMP messages aren’t blocked.
If a firewall or router filters ICMP, PMTUD breaks. You’ll notice excessive SYN retransmissions and sessions that hang indefinitely.
MSS Clamping — A Practical Fix
When ICMP messages are dropped, PMTUD fails.
To prevent this, routers and firewalls can use MSS Clamping — a method to control the TCP segment size at the start of a connection.
MSS (Maximum Segment Size) defines how much data (excluding headers) a device can receive in one TCP segment:
MSS = MTU - IP Header (20 bytes) - TCP Header (20 bytes)
For example:
- Ethernet MTU 1500 → MSS = 1460
- PPPoE MTU 1492 → MSS = 1452
By automatically clamping MSS values, you ensure packets never exceed the actual path MTU — avoiding fragmentation and broken connections.
In pfSense, this can be configured under:
Firewall > NAT > Outbound > Edit Rule → TCP MSS → Enable MSS clamping and set value (e.g., 1452)
Finding the Correct MTU
You can manually test the proper MTU using the ping command with the Don’t Fragment (DF) flag.
Reduce the packet size until the ping succeeds, then add 28 bytes for IP + ICMP headers to find your true MTU.
Windows
ping -n 1 -l 1500 -f www.example.com
Linux
ping -M do -s 1500 -c 1 www.example.com
macOS
ping -D -v -s 1500 -c 1 www.example.com
Example
C:\> ping -n 1 -l 1382 -f www.google.com
Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set.
C:\> ping -n 1 -l 1372 -f www.google.com
Reply from 172.217.25.164: bytes=68 time=25ms TTL=247
Correct MTU = 1372 + 28 = 1400
Summary
- VPN Connections: Reduce MTU to 1400–1472 to account for encapsulation overhead.
- PPPoE WAN Links: Set MTU to 1492 and clamp MSS to 1452.
- Virtual Networks (Proxmox, QEMU, VMware): Ensure bridges and vNICs share consistent MTU settings.
- Firewalls and Routers: Always allow ICMP Type 3, Code 4 (Fragmentation Needed) for PMTUD to function properly.
| Setting | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Ethernet WAN | Keep MTU at 1500, MSS 1460 |
| PPPoE WAN | MTU 1492, MSS 1452 |
| VPN Tunnel | MTU 1400–1472, MSS 1360–1432 |
| Blocked ICMP | Enable MSS Clamping |
| Path MTU Issues | Use ping testing to find optimal MTU |
MTU issues can mimic countless other problems — from broken VPNs to partial web pages. Understanding how MTU, PMTUD, and MSS Clamping interact gives you the tools to troubleshoot efficiently and stabilize network performance.
Whether you’re tuning a pfSense firewall, a Proxmox-hosted router, or a cloud VM, setting MTU and MSS correctly can eliminate frustrating, intermittent connection pr
Need help diagnosing MTU or network performance issues?
Our team can audit, optimize, and secure your connectivity — from edge routers to virtual infrastructure. Contact us to learn more about our managed network solutions and performance tuning services.